
Azure Local – Common update issues
- Intro
- Common update problems
- PowerShell modules
- Wrong drivers on network adapters
- IPv6 issue
- Python not allowed in MpPreference
- Azure Arc Bridge (ARB) is offline
- No File Found
- Failing CAU RUN
- Old cluster validation reports
- Update Readiness Critical
- Update readiness warning but failing once trying to run the actual update
Intro
There can be lots of different errors and issues around patching Azure Local. I have tried to write about all the errors I have come across so far in my work with Azure Local.
Common update problems
PowerShell modules
Sometimes having the wrong (too new or too old) version of a module in PowerShell, can stop the update from happening. Use this article as reference:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/answers/questions/2262865/powershell-module-version-check-fail-on-azure-loca
Wrong drivers on network adapters
If you are running Inbox Drivers on any network adapter used for Azure Local, this must be fixed before you can continue (install vendor-based drivers).
Use this PowerShell command to see if you have any Inbox drivers in use: Get-NetAdapter -Physical | fl *driver*
IPv6 issue
Some have reported (I have not seen this issue myself) that issues with IPv6 can cause problems.
Reference article: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/answers/questions/2287798/azure-local-deployment-failed
Command to use: Disable-NetAdapterBinding -InterfaceAlias * -ComponentID ms_tcpip6
Python not allowed in MpPreference
We need to make sure that no policy is blocking Python from creating MOC ARB files doing update Based on previous incidents I have talked to Microsoft about, these steps have worked:
- Confirm if Python are listed
Get-MpPreference | Select -ExpandProperty ControlledFolderAccessAllowedApplications - Add Python to the policy
Add-MpPreference -ControlledFolderAccessAllowedApplications “C:\Program Files (x86)\Microsoft SDKs\Azure\CLI2\python.exe”
Azure Arc Bridge (ARB) is offline
If you get an error about Azure Arc Bridge (also called MOC ARB) being offline. Check of the control-plane VM is in running state on the stack. Also try to ping the IP of the MOC.
To get the IP of the MOC, use these PowerShell commands:
Import-Module MOC
get-archciconfigOutput of the command will tell the IP address. If ping is not successful, verify that the control-plane VM has network adapter attached (use Failover cluster or HyperV), and is attached to the right VMSwitch / NetIntent and VLAN tagged if used.
No File Found
Bug in 23H2 2507 doing update to newer version. No File Found. This bug sometimes caused by issues with the folder C:\users\LCMUSER\Documents\
(Note that LCMUser is the user you choosed to deploy or update with)
Navigate to the file: “c:\Program Files\WindowsPowerShell\Modules\DownloadSdk\1.1.22\DownloadSdk.psm1”
Search in the file for “Test-DownloadSdkConfiguration”. Locate any relative path and hardcode this to another folder (e.g. C:\users\LCMUSER\)
Failing CAU RUN
If you see the error: Type ‘EvalCauRetryApplicability’ of Role ‘CAU’ raised an exception: CAU Run failed
Reference article: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/answers/questions/2121140/azure-stack-hci-update-failed
It may be because of issues with installing a feature update or hotfix update on the nodes.
Here I will share some basic info about the topic, but you can read more about it and how to use a workaround in this article:
Use the command Get-CAURUN to see if any active CAU is running on the stack.
Use Event Viewer to get details about the failed attempts from this path:
Event Viewer > Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > ClusterAwareUpdating > Admin
If you want to try installing CAU update from PowerShell, you can run a SelfUpdate by triggering CAU using PowerShell from one of the nodes. Below is an example of how to start HotfixPlugin, but please be aware that other types of CAU plugins exist and this should only be used in troubleshooting scenarios and only combined with the details of the article above
Import-Module ClusterAwareUpdating; Invoke-CauRun -ClusterName "inputClusterName" -CauPluginName 'Microsoft.HotfixPlugin' -CauPluginArguments @{ 'HotfixRootFolderPath' = '\\localhost\C$\ClusterStorage\Infrastructure_1\Shares\SU1_Infrastructure_1\CloudMedia\Platform'; 'DisableAclChecks' = 'True' } -MaxRetriesPerNode 3 -NodeOrder @( 'node01', 'node02' ) -EnableFirewallRules -FailbackMode Immediate -SuspendRetriesPerNode 5 -Force -ForceSelfUpdateYou can also read more about it on the Microsoft Learn article: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-local/update/update-troubleshooting-23h2?view=azloc-2506
Old cluster validation reports
Having old cluster validation reports on nodes can block the update from starting.
Go to “\\nodename\c$\Windows\cluster\Reports” on each node in the cluster.
Delete all files with the name like “Validation Report yyyy.mm.dd At hh.mm.ss.htm”.
Then run the command Test-Cluster in PowerShell from only one of the nodes. This will create new validation report on all nodes. If no errors are found, this will soon replicate the Azure Portal and you can start the update.
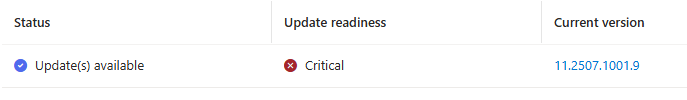
Update Readiness Critical
If you see issues with updating the stack in Azure Portal under Updates, you can use Test-Cluster to verify. You can also use Environment Check, which is a set of tools to validate all aspects of the stack.
More info can be found in the official Microsoft Learn article: https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-local/manage/use-environment-checker
But, to fix any issues regarding the “Update Readiness Critical”, you must fix the errors before proceeding with the update. In some cases, it is required to create a ticket with Microsoft to get support for the issue.
On Microsoft Learn, we can find a great article about how to troubleshoot and retry updates from PowerShell (my favorite way of working with updates for Azure Local):
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-local/update/update-troubleshooting-23h2
Here is an example case:
You want to validate if your stack is ready for an update. Use this command to see what updates are ready and not installed:
Get-SolutionUpdate | FL DisplayName, Description, ResourceId, State, PackageTypeThen you take note of the ID of the update available for installation and use it for the next command that will get details about this update (in my example, update 11.2508.1001.51 was ready to be installed)
$Update = Get-SolutionUpdate –Id "redmond/Solution11.2508.1001.51"Now start the update with the -PrepareOnly switch to ensure we only run the validation part of the process:
Get-SolutionUpdate -Id "redmond/Solution11.2508.1001.51" | Start-SolutionUpdate –PrepareOnlyIf you want to see that it is running, you can use this command to get a view of it being in running state:
Get-SolutionUpdate -Id "redmond/Solution11.2508.1001.51" | ft Version,State,UpdateStateProperties,HealthStateWait for it to be completed or failed and view outputs using the command:
Get-SolutionUpdate -Id "redmond/Solution11.2508.1001.51"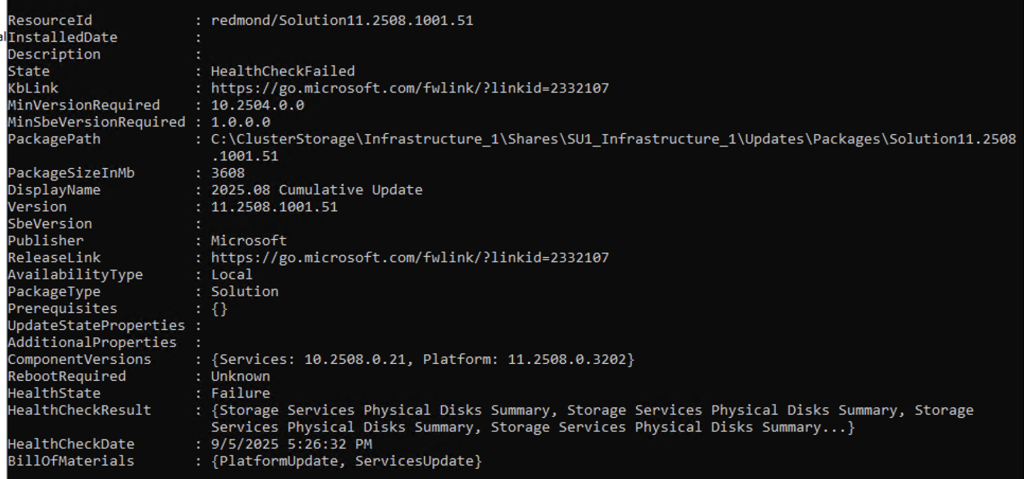
Use this command to get the all the details about each failing task:
$result = Get-SolutionUpdateEnvironment
$result.HealthCheckResult | Where-Object {$_.Status -ne "SUCCESS"} | FL Title,Status,Severity,Description,Remediation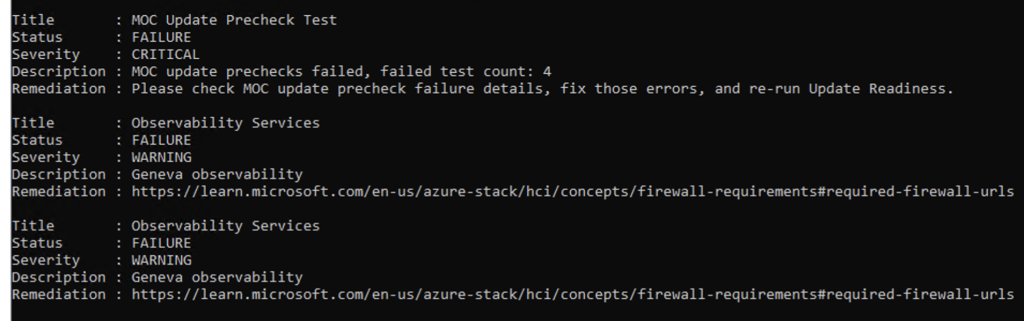
Update readiness warning but failing once trying to run the actual update
If the update validation is displaying as healthy or warning, but when the actual update starts, it is failing in the pre-check validation state right before applying the update, here is what to do (Steps are written as comment in the PowerShell commands)
# Get the update
Get-SolutionUpdate | FL DisplayName, Description, ResourceId, State, PackageType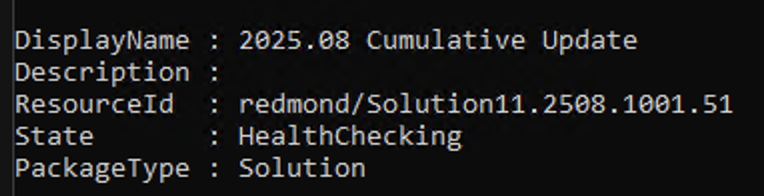
# We need to get the update run ID
Get-SolutionUpdate | Get-SolutionUpdateRun | sort TimeStarted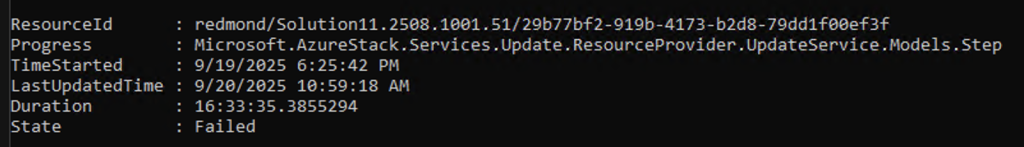
# Find the ResourceID of the update you are currently running
$results = Get-SolutionUpdate -Id "redmond/Solution11.2508.1001.51/29b77bf2-919b-4173-b2d8-79dd1f00ef3f"
$result.HealthCheckResult | Where-Object {$_.Status -ne "SUCCESS"} | FL Title,Status,Severity,Description,RemediationcodeI my case, it was failing on Az CLI version. But the Azure Portal was not helpful with remediation steps. PowerShell gave me a bit more info:
Name : AzStackHci_ValidatedRecipe_AzureCli_Version
DisplayName : Test Azure-Cli Module Version
Tags : {}
Title : Test Azure-Cli Module Version
Status : FAILURE
Severity : CRITICAL
Description : Validating that the installed version of Az.Cli is the required version.
Remediation : https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/azure-local/update/update-troubleshooting-23h2
TargetResourceID : NODENAMHERE
TargetResourceName : NODENAMEHERE
TargetResourceType : ValidatedRecipe
Timestamp : 9/19/2025 9:33:53 PM
AdditionalData : {}
HealthCheckSource : PreUpdate\Standard\Medium\ValidatedRecipe\0b53798b
So I went to the NuGet store on each node in the stack and installed the lasted Az CLI version:
C:\NugetStore\Microsoft.AzureStack.AzureCLI.2.69.0.1\content\azure-cli-2.69.0.msi
After that, I could resume the update:
Get-SolutionUpdate -Id $results.ResourceId | Start-SolutionUpdateHave feedback on this post?
Send me a message and I'll get back to you.